

Generation of contours is conditioned by visualisation, which enforces the use of cartographic generalisation rules.Contours are a non-continuous representation of the terrain, in which the surface forms between the selected contour interval are unknown.While contours are still a valid method for visualising topography, from the perspective of data storage, they have two deficiencies: Before the diffusion of using DEMs, country-wide elevation data was stored on the contour lines in printing plates and paper maps.
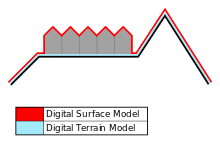

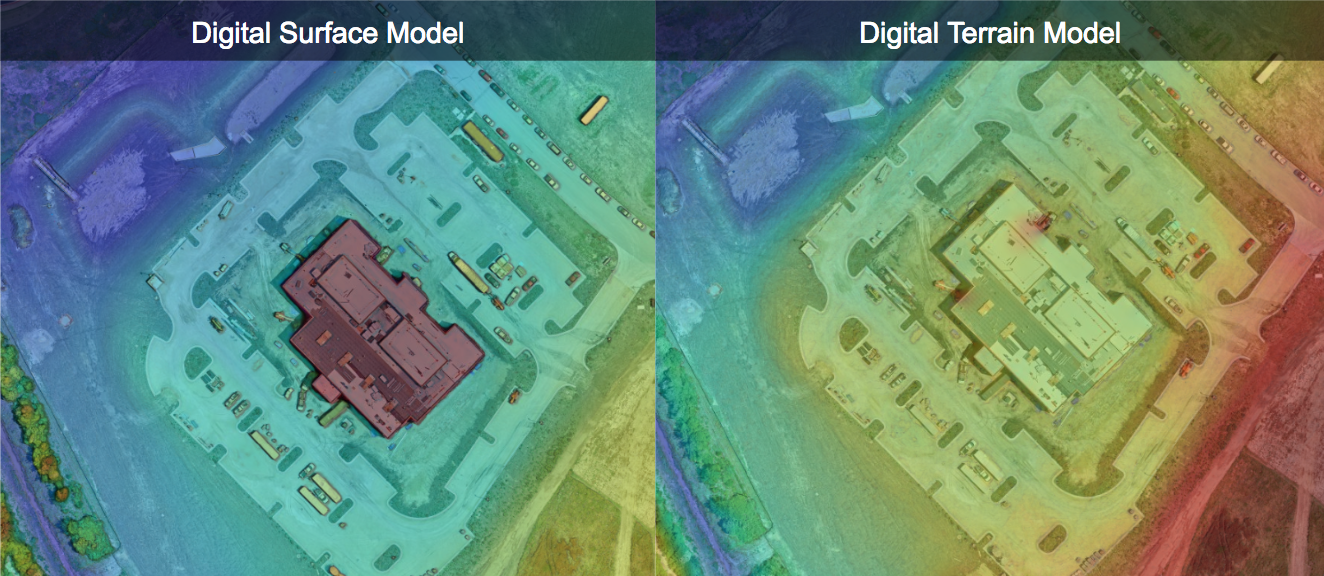
Thus, DSM represents the Earth’s surface only in open areas, while in other regions the model follows the forest canopy and the roofs of buildings.ĭigital Elevation Model (DEM) is an invention that has liberated gathering and storing of elevation data from the principles of traditional cartography. It means a model that represents the highest elevation of the terrain. The most important element of DTM is DEM.ĭigital Surface Model (DSM) is a concept that has become common due to widespread use of airborne laser scanning. In a discussion related to DEMs, common terms are Digital Terrain Model (DTM) and Digital Surface Model (DSM).ĭigital Terrain Model (DTM) is a model that represents the Earth’s surface together with other topographic information, such as data about land cover, slopes, and aspects of the terrain. Typically, DEM is stored in a data system as a regular grid or a triangulated irregular network (TIN). Robotics and Intelligent Transportation Systemsĭigital Elevation Model (DEM) is a numerical representation of the Earth’s surface that contains actual height points representing the topography, as well as the method to calculate elevations between the height points.Spatial Data Solutions Supporting Digitalisation.Centre of Excellence in Laser Scanning Research.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
